Twig templates internationalization
<p>Hello world!</p>
⬇
<p>{{ 'hello_world'|trans }}</p>
<!-- translations/messages.en.yaml: hello_world: 'Hello world!' -->
<p>Hello world, {{ user }}!</p>
⬇
<p>{{ 'hello_world'|trans({'user': user}) }}</p>
<!-- translations/messages.en.yaml: hello_world: 'Hello world, {user}!' -->
<p>Hello <b>world</b>!</p>
⬇
<p>{{ 'hello_world'|trans|raw }}</p>
<!-- translations/messages.en.yaml: hello_world: 'Hello <b>world</b>!' -->Features supported
- Hardcoded strings extraction
- Automatically extract strings in bulk
- Extract selection
- Inline tag extraction
- Register a missing key
- Navigation to translation
- Localization hints
- Rename keys and placeholders
- Ignore strings by content
Configure hardcoded strings extraction from Twig templates
The plugin should automatically configure itself for Symfony projects, but adjustments could be needed for custom setup and other frameworks.
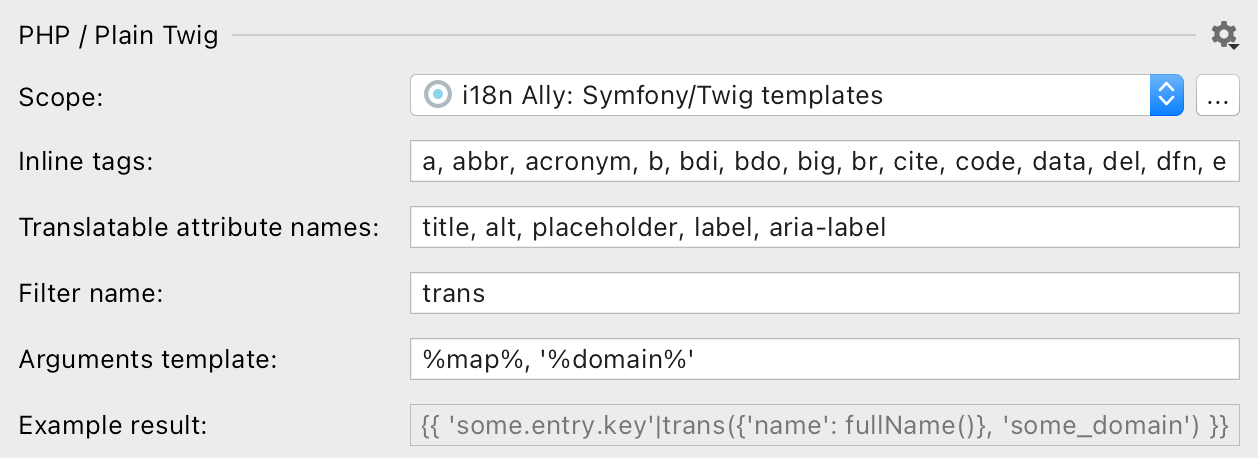
Scope
i18n Ally is applying inspections for files that have .twig extension and are included into
a PhpStorm’s scope.
Create a new scope or adjust existing by clicking on … button and handpicking only the meaningful directories and files.
Select Project files to include all .twig files in your project.
Inline tags
List of tags that would be taken inside translations, like a, strong or span. Filled by default with
all “inline” tags listed on MDN.
An example of extraction result difference between block and inline tags:
Three
<p>different</p>
keys.
<!-- ⬇ will be extracted into -->
{{ 'three'|trans }}
<p>{{ 'different'|trans }}</p>
{{ 'keys'|trans }}
One <b>inclusive</b> keys.
<!-- ⬇ will be extracted into -->
{{ 'one_inclusive_key'|trans|raw }}Notice the raw filter appended to the key that contains inline tags. i18n Ally adds it automatically to ensure current rendering of the content.
You can add custom tags, like icon, by appending a new tag to the comma-separated list.
Translatable attribute names
Translatable attributes are also checked for the translatable text:
<img src="…"
alt="Checked by default"
title="Checked by default"
data-content="Requires configuration" />You can add custom attributes, like data-content, by appending a new attribute to the comma-separated list.
Filter name
Filter name to use for extraction is the default one in Symfony framework: trans would become 'key'|trans.
If you have a custom function or an array for fetching translations you create a custom filter:
$filter = new \Twig\TwigFilter('translate', function ($key, $domain = 'messages') {
textdomain($domain);
return gettext($key);
});Replacement template
The “Replacement template” reflects the result of the hardcoded string extraction.function name and arguments template.
Recommended value for Symfony 3+: trans(%map%, '%namespace%')
with “Skip default namespace” checkbox set to true.
%key% (not available for Twig)
Short key or a natural language string that defines a translation.
%namespace%
Namespace (called ‘domain’ in Symfony) usually means a part of language file path from where translations would be searched for. The default
namespace is usually messages, but could be changed by putting a namespace in first position in “Namespaces” field.
%map%
If there are no variables in the string, then nothing would be added.
Map will be replaced with a hash if there are any placeholders detected:
{{ 'key'|trans({'foo': foo, 'bar': bar}, 'namespace') }}.
Placeholder names will be determined automatically based on a respective variable, function or method name.
In language files placeholder syntax will be determined based on the Placeholder format setting of the language file.
%list%
If there are no variables in the string, then nothing would be added.
List will be replaced with an array if there are any placeholders detected:
{{ 'key'|trans([foo, bar], 'namespace') }}.
In language files the ordered placeholder syntax {0}, {1} will be enforced.
%varargs%
If there are no variables in the string, then nothing would be added.
Varargs will be replaced with placeholder passed directly to the translation function if there are any placeholders detected:
{{ 'key'|trans(foo, bar, 'namespace') }}.
In language files the ordered placeholder syntax {0}, {1} will be enforced.
Supported language constructs
All strings inside tags and translatable attributes are checked.
What’s not supported
- Strings inside twig expressions, like
{% set var = 'Hello!' %} - Extraction with function, like
{{ trans('key') %}, or array, like{{ lang.key %} - Extraction with
transblocks
What strings are skipped
- Pure HTML markup with Twig expressions, like
<a href="{{ route('home') }}"><img …></a>. - All attributes except ones listed in “Translatable attribute names” preference.
- Content inside
transblock as it’s assumed to be already extracted. - Content inside
verbatimtag. - Content inside
scriptandpretags. - Strings that looks like code: without letters, multiple words without spaces or
camelCasedones.
Best practice: dealing with branching in messages
It’s common to have small and simple branching for presentation purposes:
Webhook <strong>{% if success %}succeeded{% else %}failed{% endif %}</strong>.The best practice it to separate this message into two different ones so translators would have a full context and would be able to adjust word order according the target language grammar.
1st step: manually extract the condition out of the message to get two messages without condition
{% if success %}
Webhook <strong>succeeded</strong>.
{% else %}
Webhook <strong>failed</strong>.
{% endif %}2nd step: replace simple messages with i18n Ally
{% if success %}
{{ 'webhook_succeeded'|trans|raw }}
{% else %}
{{ 'webhook_failed'|trans|raw }}
{% endif %}